Our Services
Scans & Diagnostics
Precision in Diagnostics, Excellence in Care
We offer a comprehensive range of advanced imaging and laboratory tests to ensure accurate diagnoses and better health outcomes. With state-of-the-art technology and a team of expert radiologists and pathologists, we are committed to delivering fast, reliable, and precise results for all your diagnostic needs.

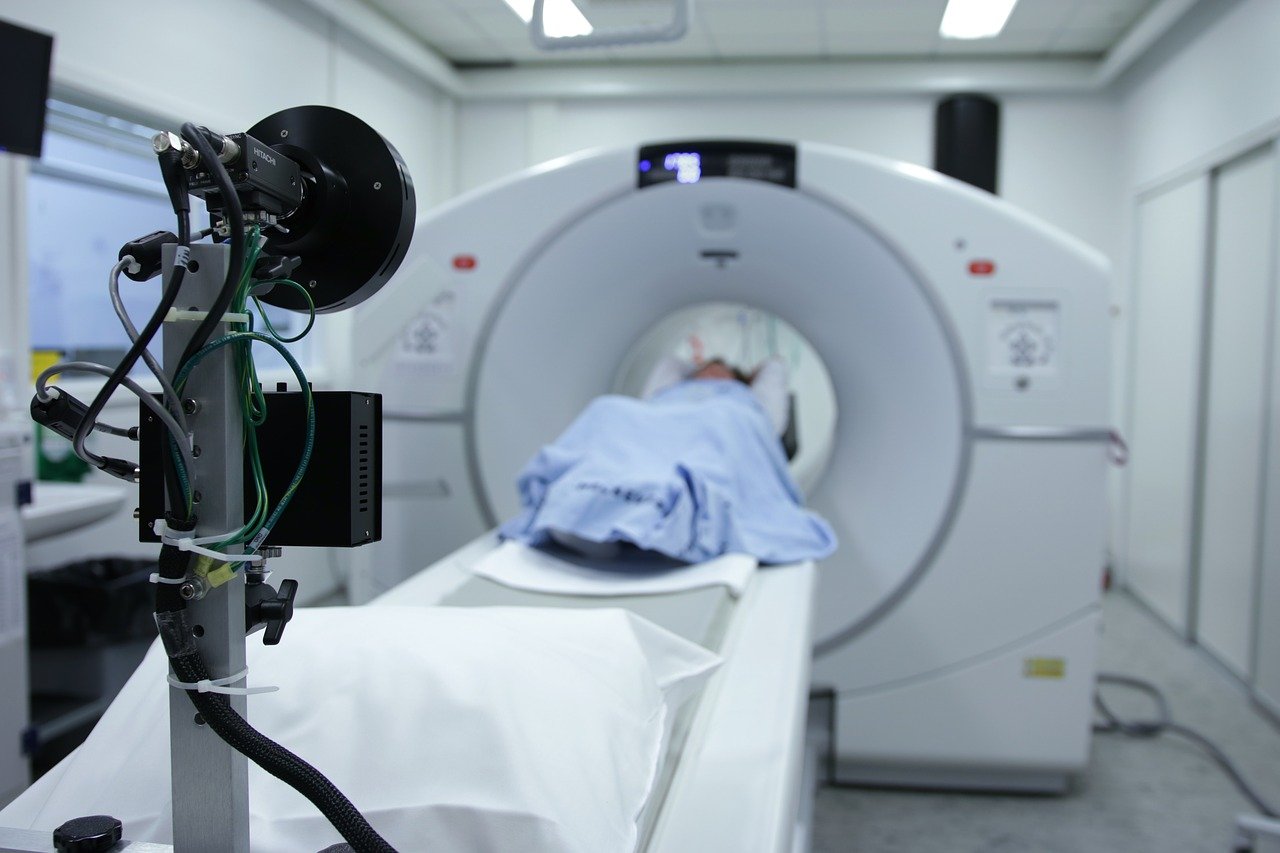
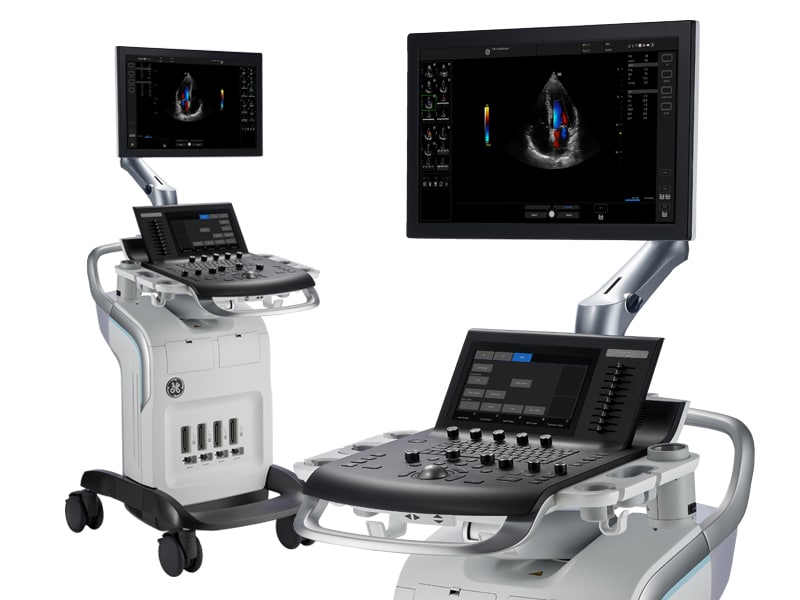


CT-Scan 32 slice

A 32-slice CT scan is a type of computed tomography (CT) scanner that captures 32 cross-sectional images (slices) of the body per rotation. It provides detailed, high-resolution images of internal structures, including bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues, making it useful for various medical diagnoses.
Head
A 32-slice CT scan of the head provides detailed, high-quality imaging that is crucial for diagnosing and evaluating various conditions affecting the brain, skull, and sinuses.
Spine
A 32-slice CT scan of the spine provides rapid, high-resolution imaging, essential for diagnosing a wide range of spinal conditions, including trauma, degeneration, tumors, and disc disorders.
Neck
Limb
Chest
A 32-slice CT scan of the chest uses computed tomography to create detailed cross-sectional images of the lungs, heart, blood vessels, and ribs.
Abdomen
A 32-slice CT scan of the abdomen captures high-resolution cross-sectional images of the stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, kidneys, and pancreas using computed tomography.
4D Ultrasound & Doppler
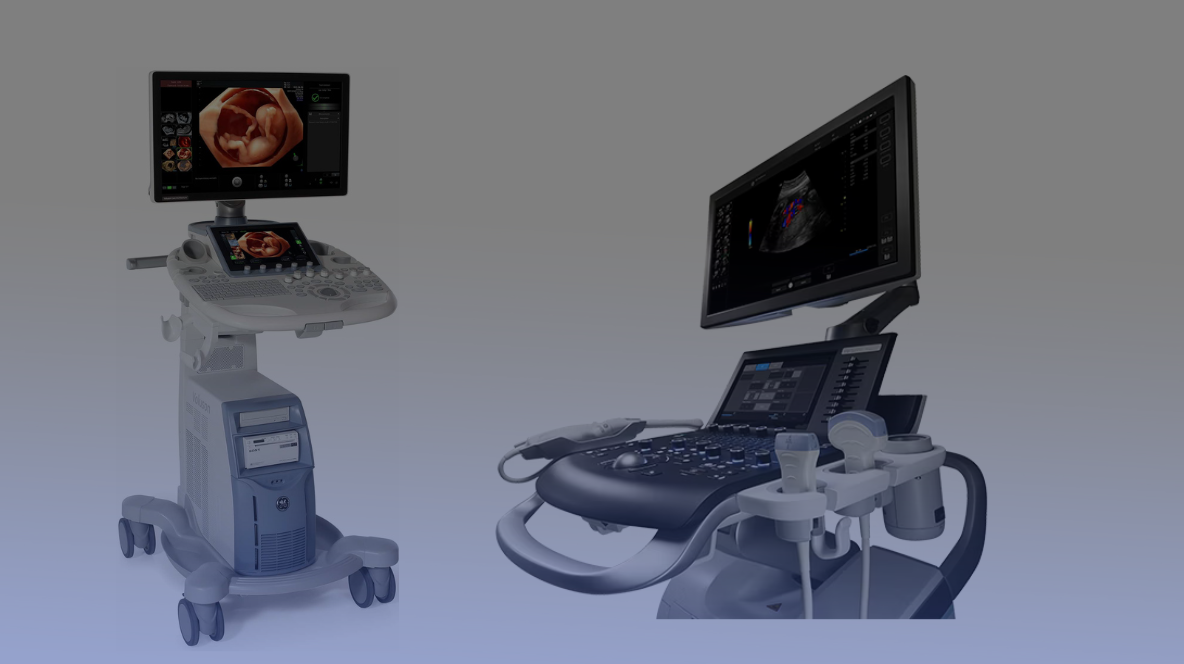
A 4D ultrasound is an advanced medical imaging technique that provides real-time, three-dimensional (3D) images with motion (4D). Unlike traditional 2D and 3D ultrasounds, which offer static images, 4D ultrasound captures continuous movement, allowing doctors and parents to see live, moving images of a baby in the womb or internal organs in action.
General abdomen & pelvis
A 4D Ultrasound & Doppler scan of the abdomen and pelvis offers real-time, high-resolution imaging of internal organs and blood flow, aiding in the diagnosis of abdominal, pelvic, and vascular conditions.
Breast
A 4D Ultrasound & Doppler scan of the breast provides dynamic imaging for assessing lumps, cysts, tumors, and blood flow, helping diagnose conditions like breast cancer, benign disorders, and infections.
Renal Doppler
Renal Doppler is an ultrasound-based technique that assesses blood flow in the kidneys and renal arteries, used to evaluate kidney function and detect vascular abnormalities affecting renal health.
Neck
Scrotum
Carotid Doppler
Thyroid
A 4D Ultrasound & Doppler scan of the thyroid provides real-time, high-resolution imaging for diagnosing nodules, goiter, cancer, and inflammation, while assessing blood flow to the gland.
NSG (Neurosonography)
Chest
A 4D Ultrasound & Doppler scan of the chest offers real-time imaging of cardiac, vascular, and pulmonary structures, essential for diagnosing heart disease, vascular blockages, and lung disorders.
Limb Doppler
Limb Doppler is an ultrasound-based imaging technique that assesses blood flow in the arteries and veins of the limbs, useful for evaluating vascular conditions like blockages, narrowing, or abnormal blood flow.
Digital Radiography(X Ray)

Digital Radiography (DR) is an advanced form of X-ray imaging that captures digital images directly onto a computer, eliminating the need for traditional film-based X-rays. It provides faster image processing, improved image quality, and reduced radiation exposure, making it a widely used diagnostic tool in modern medicine.
Head
Digital Radiography (X-ray) of the head is a non-invasive technique that captures high-resolution images of the skull, brain, sinuses, facial bones, and teeth, commonly used for diagnosing various head conditions.
LS Spine
Digital Radiography (X-ray) of the LS spine is essential for diagnosing fractures, degenerative diseases, herniated discs, spinal deformities, and other abnormalities, providing clear and fast imaging for effective diagnosis and treatment planning.
Neck
Upper Limb
Abdomen
Digital Radiography (X-ray) of the abdomen captures detailed images of the abdominal organs, intestines, stomach, liver, kidneys, spleen, and pelvis, commonly used to diagnose various abdominal conditions.
Lower Limb
Chest
Digital Radiography (X-ray) of the chest captures high-resolution images of the lungs, heart, rib cage, and mediastinum, commonly used to evaluate various chest conditions.
HEMATOLOGY

Hematology is the branch of medical science that focuses on the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood disorders. It involves diagnosing and treating conditions related to red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), platelets, bone marrow, and the clotting system.
Complete Blood Picture (CBP)
A Complete Blood Picture (CBP) is an essential test in hematology that provides valuable insights into blood health and can help diagnose various infections, anemias, blood disorders, and nutritional deficiencies.
Blood Grouping & Typing
Blood grouping and typing are essential for determining an individual’s blood type, ensuring safe blood transfusions, managing Rh incompatibility during pregnancy, and facilitating organ transplantation.
ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate)
ESR is a useful tool for detecting inflammation, monitoring disease activity, and screening for certain infections or cancers. However, it is often used alongside other tests to provide a more complete diagnostic picture.
Platelet Count
CT (Computed Tomography)
Hemoglobin(Hb)
Hemoglobin (Hb) levels are crucial for diagnosing and monitoring anemia, polycythemia, and chronic conditions. They reflect the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity and are key in assessing health and diagnosing underlying diseases.
BT (Bleeding Time)
MP (PV & SF)
MP refers to Malaria Parasite, and PV & SF stand for Plasmodium Vivax and Plasmodium Falciparum.MP (PV & SF) is used to diagnose and differentiate between Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum malaria, enabling appropriate treatment to prevent complications.
PT (Prothrombin Time)
PT is a key test in evaluating blood clotting and coagulation disorders. It is especially important for monitoring anticoagulant therapy and assessing liver function or vitamin K deficiency.
BIOCHEMISTRY

Biochemistry is the branch of science that studies the chemical processes and substances within living organisms. It combines biology and chemistry to understand how cells and organs function at a molecular level.
Liver
The liver function tests assess liver health: ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase) and ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase) indicate liver and bone conditions, GGT(Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase) detects liver damage, and TP (Total Protein) including Albumin measures protein levels for fluid balance. Abnormal levels may signal liver disease or infections.
Others
These markers help diagnose various conditions: Blood Glucose & HbA1C for diabetes, CRP & HS-CRP for inflammation, D-dimer & FDP for clot disorders, RF, ASO, CCP & SAA for autoimmune diseases, LIP & AMS for pancreatic function, Co2-CP for acid-base balance, IgA, IgM, IgG, C3 & C4 for immunity, and PGI & PGII for gastric health.
Heart
Lipids
This test is related to lipid (fat) metabolism and cardiovascular health. A Lipid Profile measures cholesterol and triglycerides. Lipoproteins transport fats in the blood. Apo A1 is linked to “good” HDL cholesterol, while Apo B is associated with “bad” LDL cholesterol. Lp(a) (Lipoprotein(a)) is a genetic risk factor for heart disease.
Kidney
The tests related to kidney function tests are BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen), Creatinine, and Urea assess waste removal efficiency. Cys-C (Cystatin C) and NGAL (Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin) help detect early kidney damage. M ALB (Microalbumin), Beta 2-MG (Beta-2 Microglobulin), and RBP (Retinol-Binding Protein) indicate kidney filtration issues and potential disease progression.
URINE ANALYSIS
Urine Analysis (Urinalysis) is a routine laboratory test that examines a urine sample to assess overall health and detect diseases affecting the kidneys, liver, urinary tract, and metabolic system. It helps in diagnosing conditions such as infections, kidney disease, diabetes, and dehydration.
Urobilinogen
Urobilinogen is a byproduct of bilirubin breakdown and is analyzed in urine tests to assess liver function and bile flow. Abnormal levels may indicate liver disease, hemolysis, or bile duct obstruction.
Microalbumin
Microalbumin in urine helps detect early kidney damage, especially in diabetes and hypertension. Elevated levels may indicate kidney disease, requiring further monitoring and management.
Leukocytes
Leukocytes (white blood cells) in urine indicate infection or inflammation in the urinary tract. Elevated levels are commonly seen in urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney infections, or other inflammatory conditions affecting the urinary system.
Bilirubin
Blood
Specific gravity
Ketones
Ketones in urine indicate fat breakdown for energy, often due to fasting, diabetes, or low-carb diets. High levels may signal diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious condition requiring urgent medical attention.
Protein
Glucose
Creatinine
Creatinine in urine helps assess kidney function and muscle metabolism. Its levels are used to evaluate kidney filtration efficiency, with abnormal values indicating possible kidney disease or muscle disorders.
Nitrite
Nitrites in urine suggest a bacterial infection, particularly from gram-negative bacteria like E. coli. These bacteria convert urinary nitrate to nitrite, making its presence a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI).
VC (Vitamins C)
VC (Vitamins C) in urine is used to check for excess vitamin C intake. High levels can sometimes interfere with urine tests for glucose and blood, but they generally don’t indicate a health problem unless taken in very large amounts.
ELECTROLYTE ANALYSIS
Electrolyte Analysis is a laboratory test that measures the levels of essential minerals (electrolytes) in the blood, which help regulate vital body functions like fluid balance, nerve signaling, and muscle contractions. Electrolytes include sodium (Na⁺), potassium (K⁺), chloride (Cl⁻), bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻), calcium (Ca²⁺), and magnesium (Mg²⁺).
Serum electrolytes
Serum electrolytes include sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate, which are essential for maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle function. Imbalances may indicate dehydration, kidney problems, heart issues, or hormonal disorders.
Serum Calcium
pH
pH in urine measures its acidity or alkalinity. It helps assess kidney function and overall health, as diet, hydration, and certain medical conditions can affect urine pH. Abnormal levels may indicate infections, kidney stones, or metabolic disorders.
MICROBIOLOGY

Microbiology is the branch of science that focuses on the study of microorganisms, which are tiny living organisms that can only be seen under a microscope. This field covers a wide range of microbes, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae, and investigates their characteristics, behavior, and role in human health, disease, and the environment.
HIV
The HIV test detects the virus or antibodies, with types like antibody, antigen/antibody, and nucleic acid tests (NAT). Early detection helps manage the condition with antiretroviral therapy.
Widal
The Widal test is used to diagnose typhoid fever by detecting antibodies against Salmonella bacteria in the blood. It helps identify infections caused by Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi.
Hepatitis B
Dengue test
HCV (Hepatitis C Virus)
HCV (Hepatitis C Virus) is a bloodborne virus that causes liver inflammation, potentially leading to cirrhosis or liver cancer. An HCV test detects antibodies or the virus itself, helping diagnose infection and guide treatment options.
MP (Malaria Parasite) test
VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory)
The VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) test screens for syphilis by detecting antibodies, though it can sometimes give false positives.
Denta scan(CBCT)

Denta Scan, or Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), is a specialized 3D imaging technique used in dentistry and maxillofacial imaging. Unlike conventional dental X-rays, CBCT provides high-resolution, three-dimensional images of teeth, jawbones, nerves, and soft tissues, allowing for precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
2D Echo

2D Echo (Two-Dimensional Echocardiography) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to evaluate the structure and function of the heart using high-frequency ultrasound waves. It provides real-time, moving images of the heart, helping doctors assess heart health and detect abnormalities.
ECG
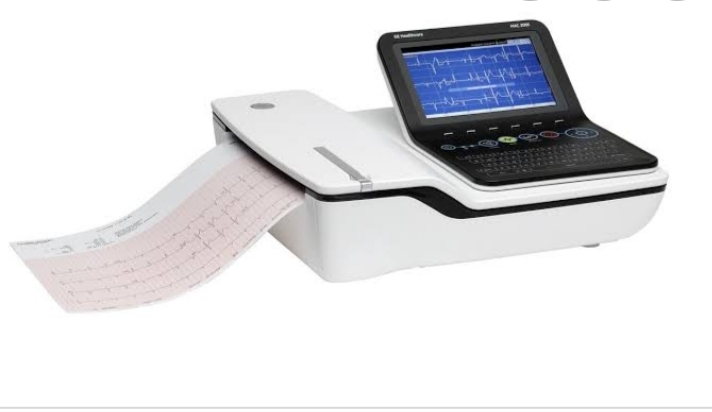
An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. It helps in diagnosing various heart conditions by detecting irregular heart rhythms, heart attacks, and other cardiac abnormalities.
Accurate Diagnostics for a Healthier Tomorrow!
Get precise, reliable, and fast results with our advanced imaging and lab tests. Trust our expert team and cutting-edge technology for your health needs.
Testimonials
